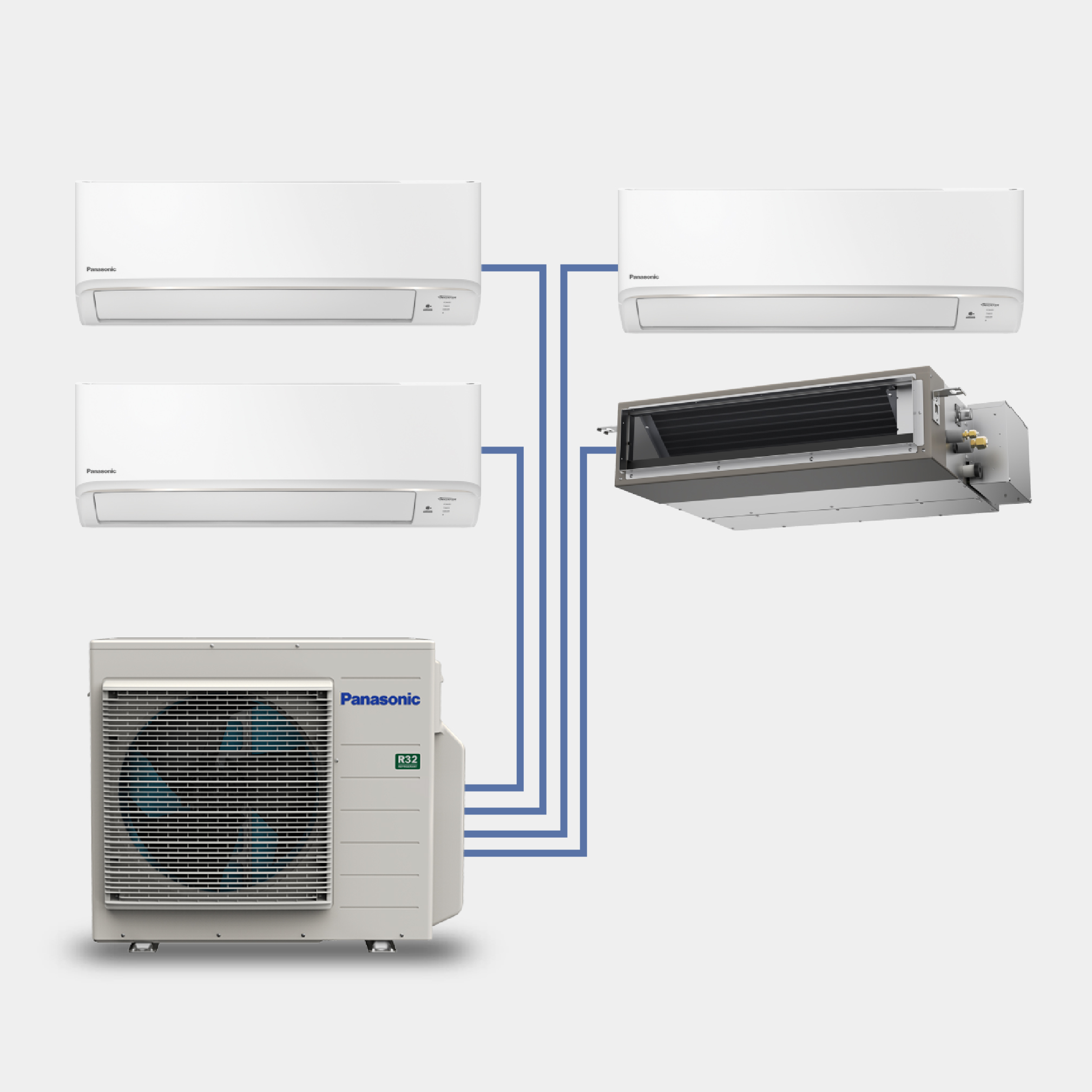
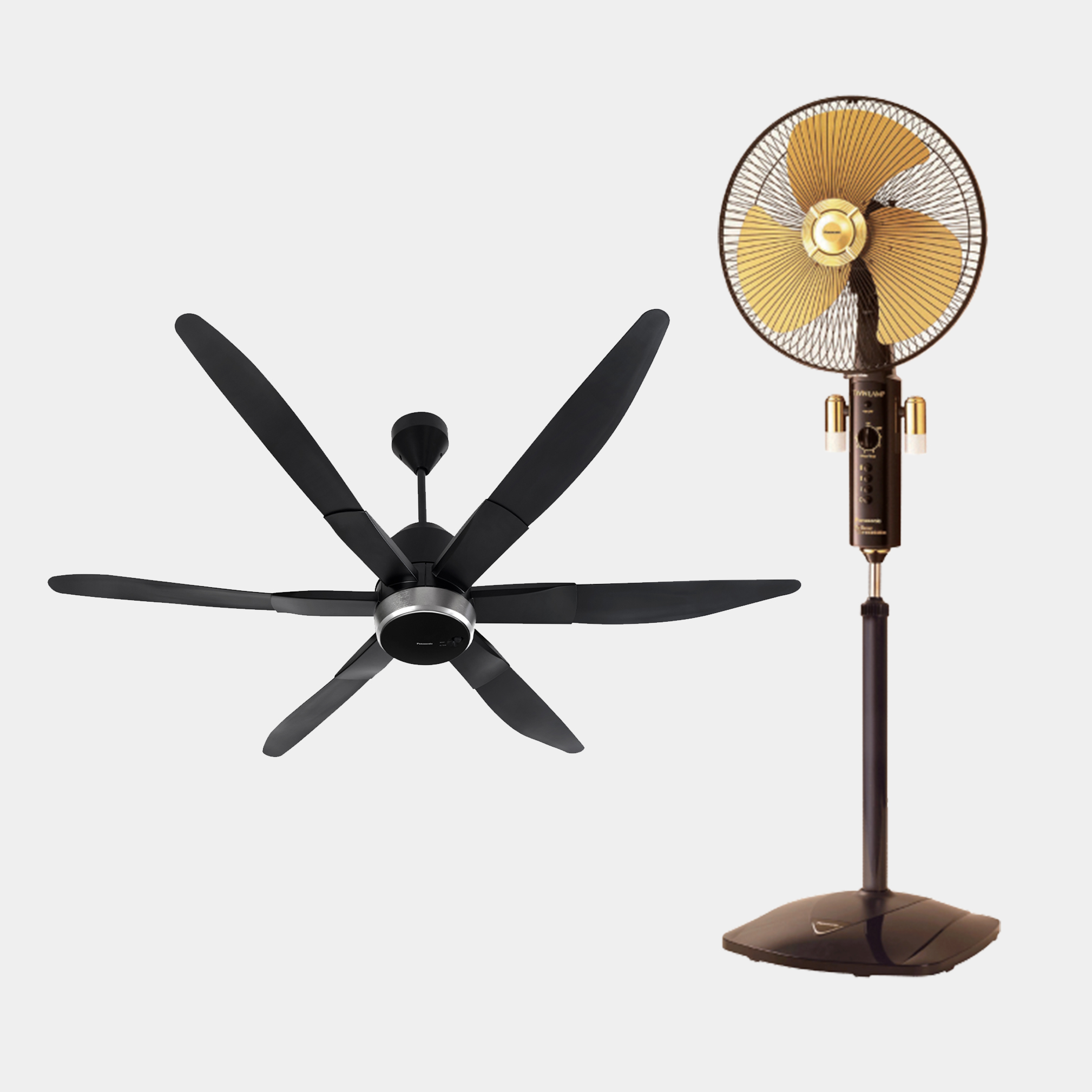
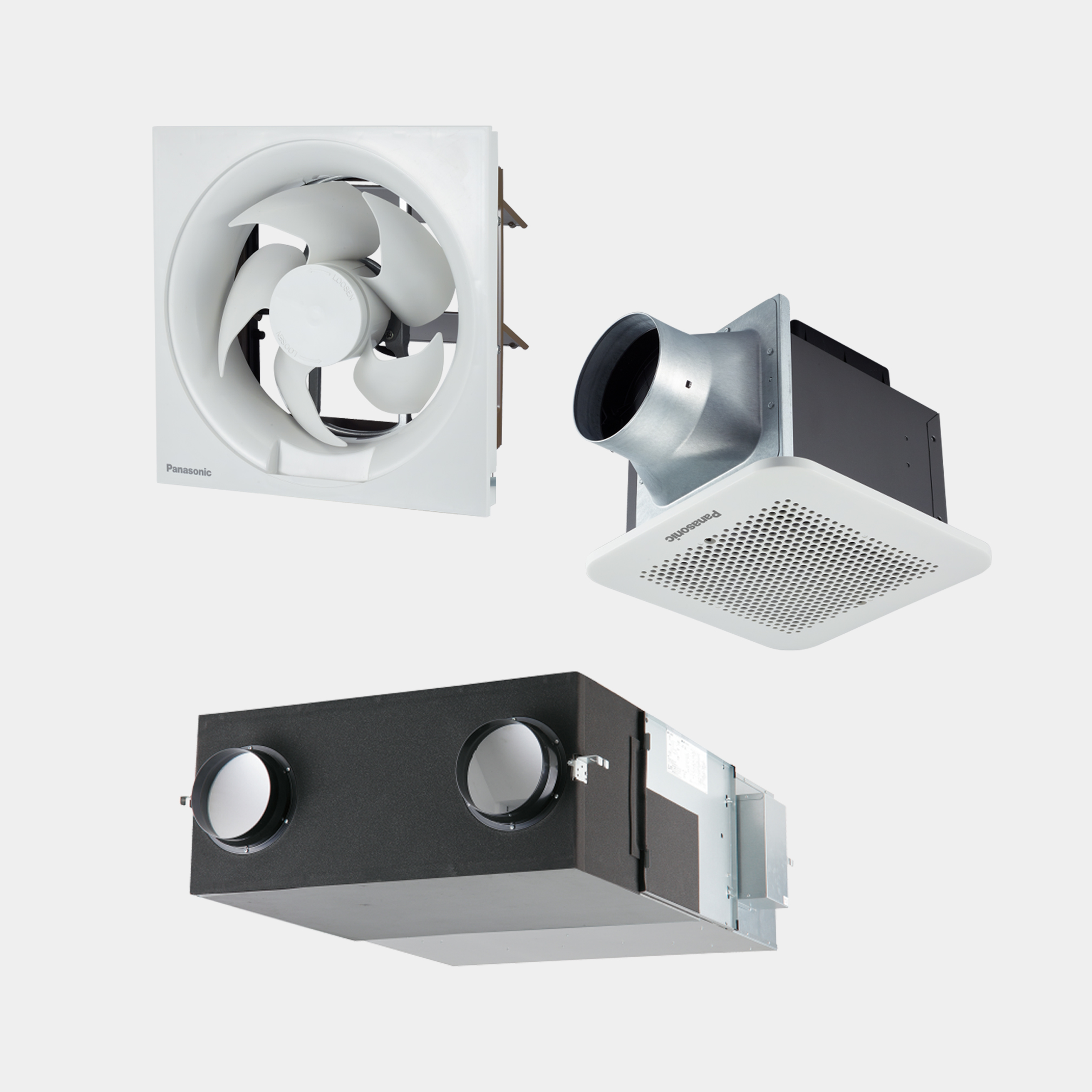
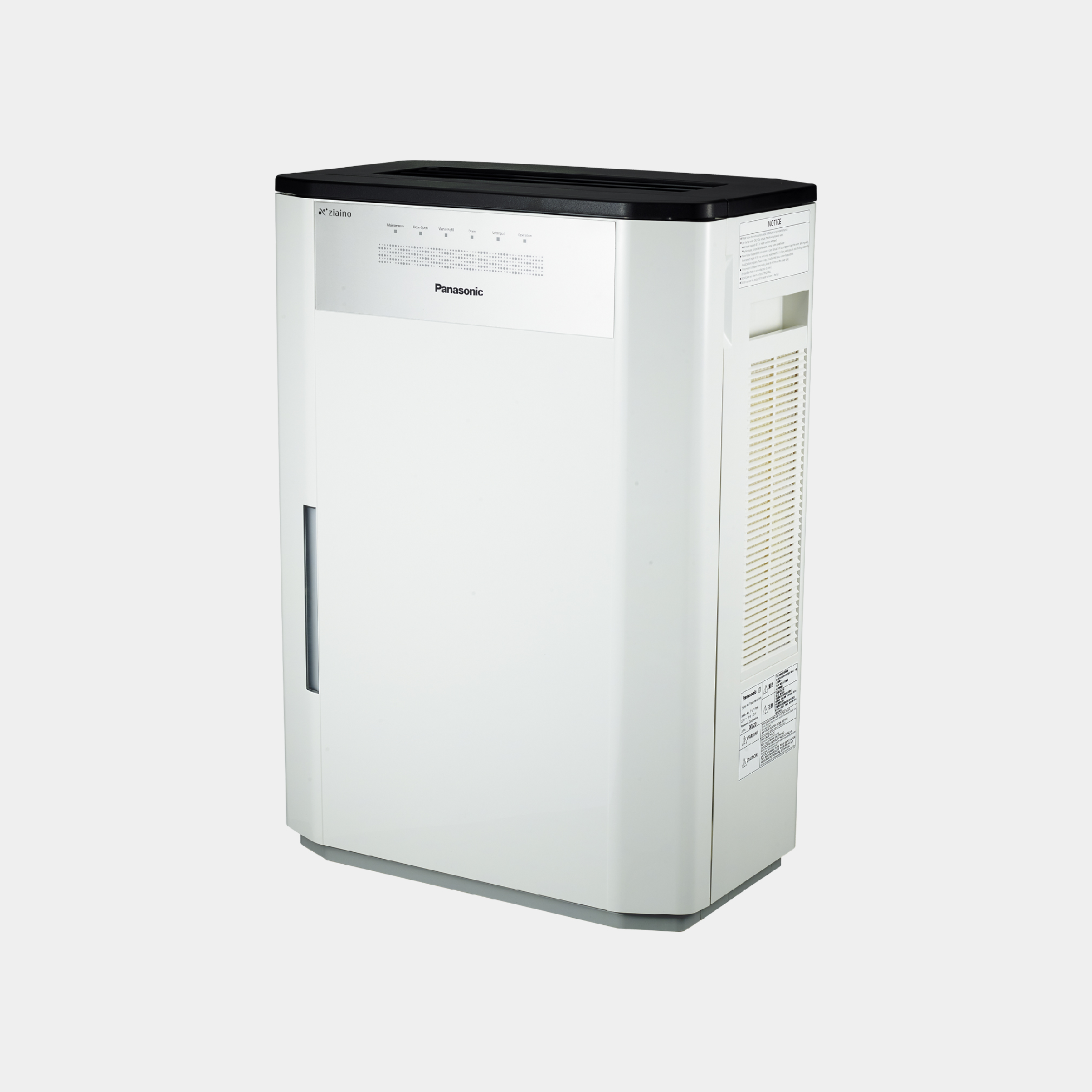
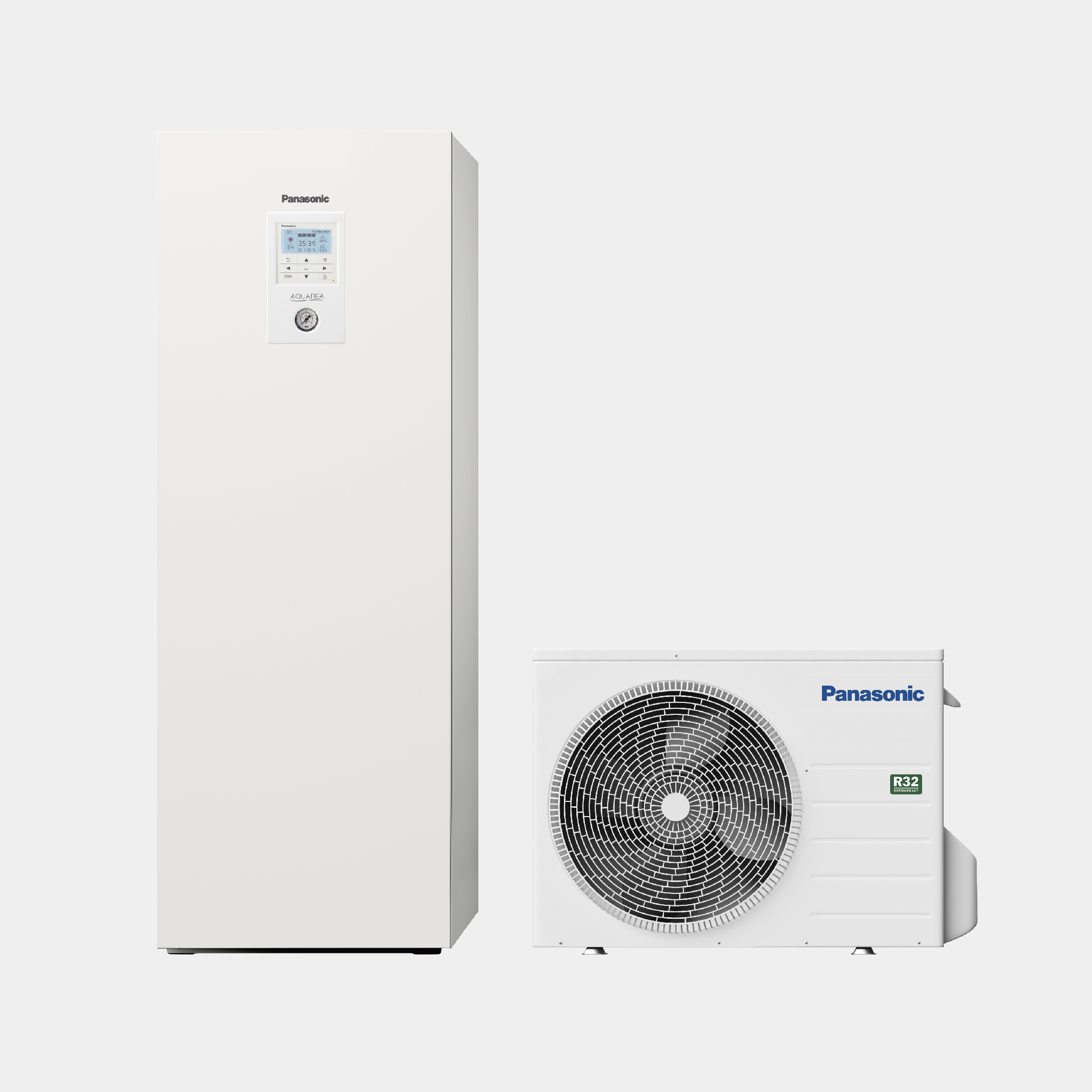
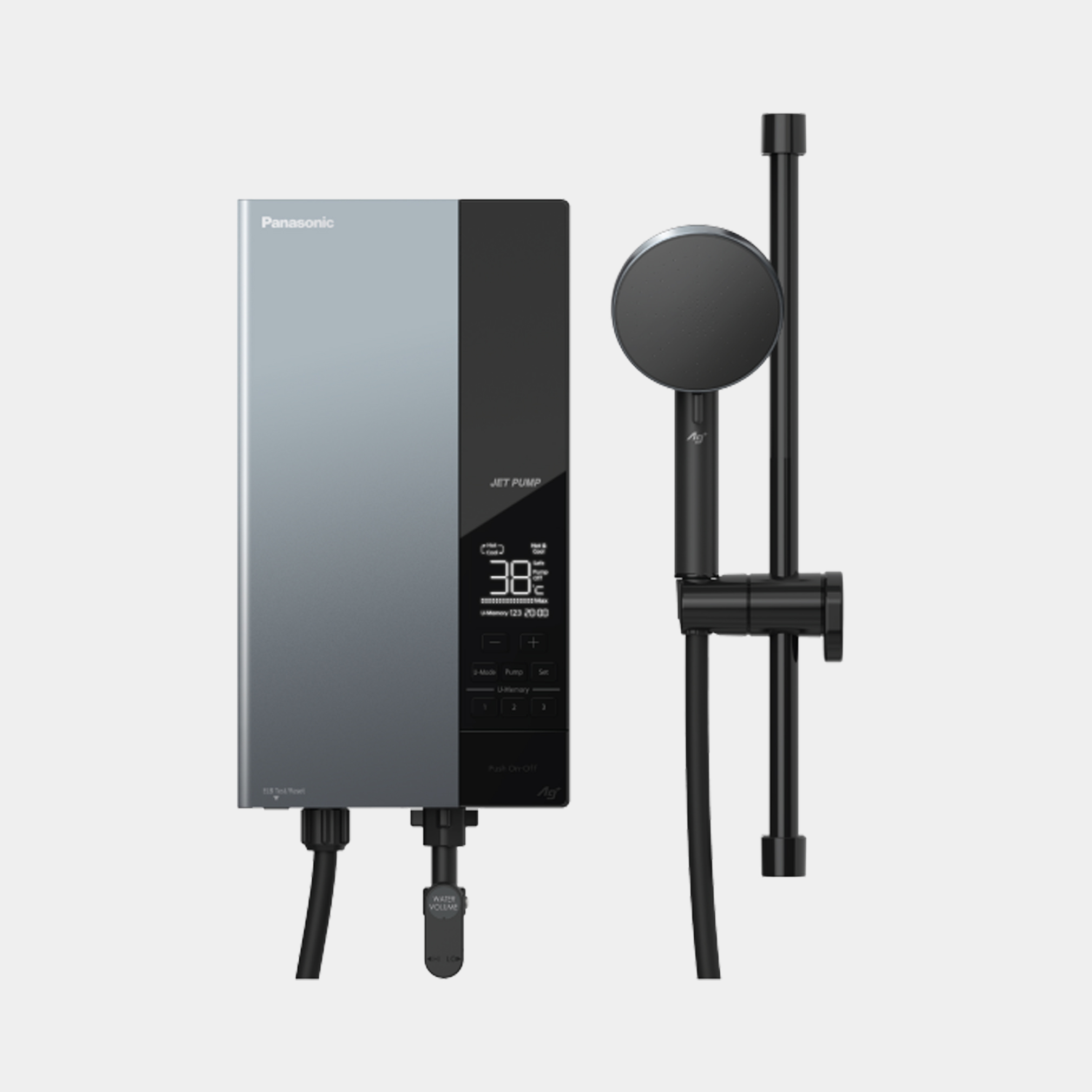
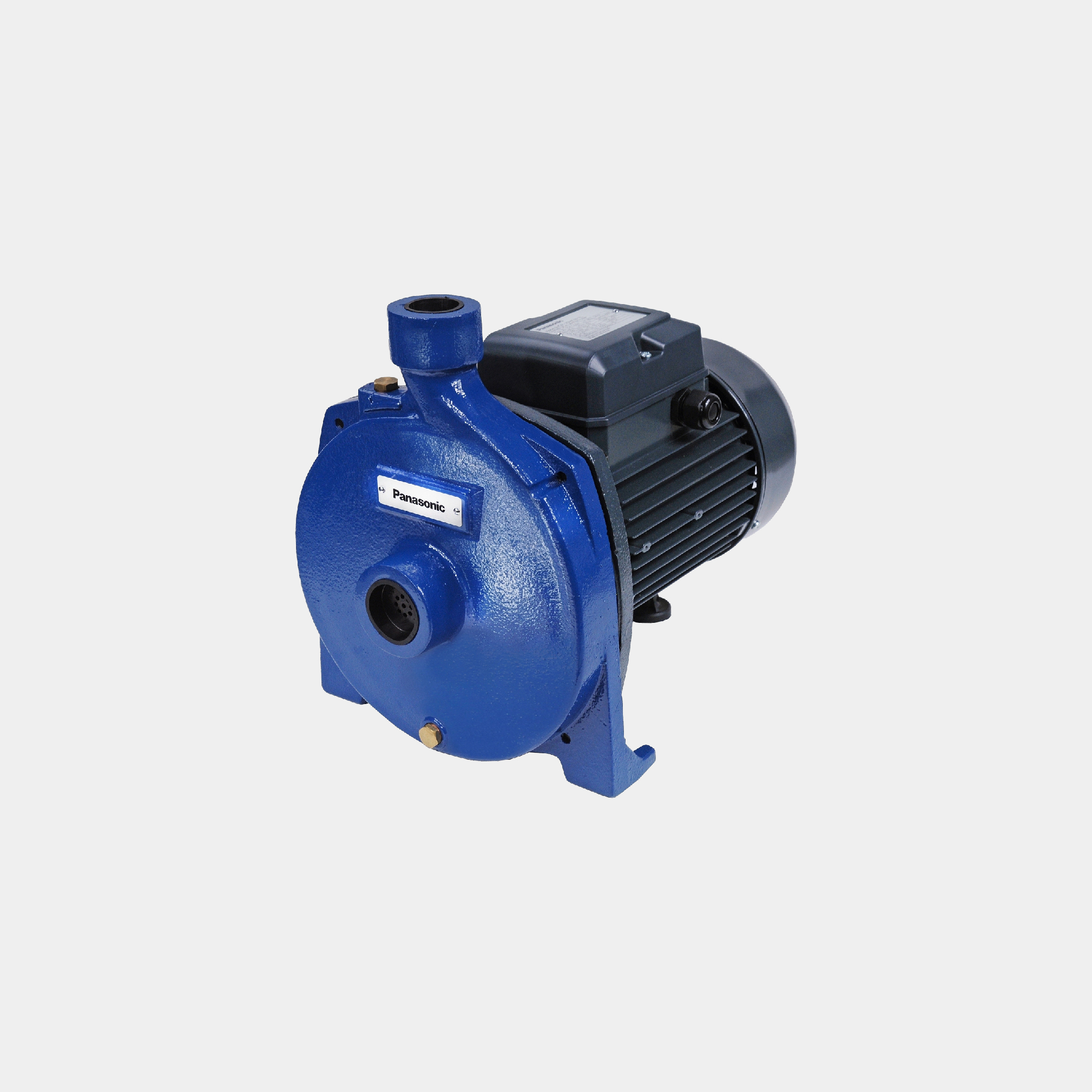
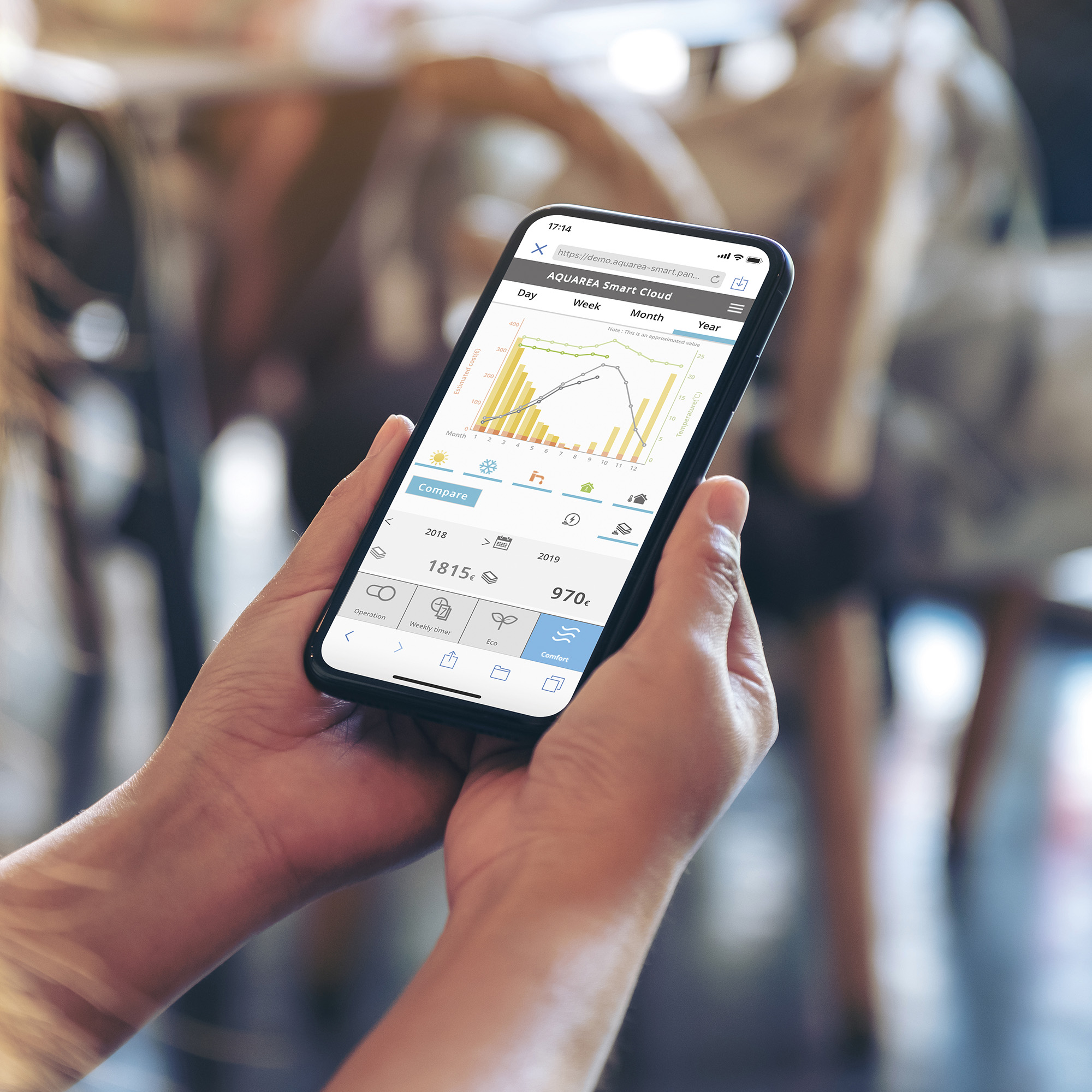
We offer a wide range of household and commercial products including air conditioners, fans, ventilation fans, air-quality appliances, water solutions, and IoT cloud solutions. Leveraging our proprietary environmental technologies, our various air and water-related products and businesses are operated on a global scale.