Realizing a Circular Society
Realizing a Circular Society
Policy
As a company that uses large amounts of natural resources in its business, we believe that using the earth’s limited resources in a sustainable manner and passing them on to the next generation is crucial. For the future of children born today, we are increasing recycling to reduce the consumption of new natural resources while reducing waste to lower our environmental impact. We are also working to reduce CO2 emissions related to the production of materials and disposal of products. We will advance these efforts in tandem with our commitment to achieving decarbonization.
Policy
As a company that uses large amounts of natural resources in its business, we believe that using the earth’s limited resources in a sustainable manner and passing them on to the next generation is crucial. For the future of children born today, we are increasing recycling to reduce the consumption of new natural resources while reducing waste to lower our environmental impact. We are also working to reduce CO2 emissions related to the production of materials and disposal of products. We will advance these efforts in tandem with our commitment to achieving decarbonization.
Increasing recycling
Utilization of recycled materials
In the production of batteries, Panasonic Energy is working to build a recycling scheme throughout the entire supply chain by reducing natural resource consumption and waste, for example by strengthening our efforts to collect and recycle waste materials from the production process as well as used products and utilize them as recycled materials.
Going forward, we will continue to promote the use of recycled materials as electrode materials, aiming not only to decarbonize our products, but also to realize a recycling-oriented society.

Recycling scheme throughout the entire supply chain
Initiatives related to secondary batteries
Initiatives related to collecting and recycling secondary batteries
For secondary batteries, countries around the world are developing legal systems and mechanisms for recycling aimed at using resources more effectively and preventing environmental pollution. In Japan, we are a member of Japan Portable Rechargeable Battery Recycling Center (JBRC), a recycling promotion organization established mainly by Matsushita Battery Industrial Co., Ltd. and SANYO Electric Co., Ltd. (our predecessors). In this role, we engage in collection and recycling of secondary batteries from cooperating stores, municipalities, and businesses nationwide. In fiscal 2025, the industry as a whole collected and recycled 1,400 tons of secondary batteries (around 50% of which were made by our company). In North America, we collaborated with other battery manufacturers to launch the Call2Recycle program, which offers recycling schemes for secondary batteries in the United States and Canada. We are also helping various other countries create the most efficient recycling systems that match the actual recycling infrastructure situation in each country.
Initiatives to establish a recycling scheme
We have signed a purchase agreement with Redwood Materials Inc., a U.S. battery recycling company, for the use of recycled cathode materials for Li-ion batteries for EVs. Under the agreement, we will establish a system to recycle process waste and used batteries into cathode materials for Li-ion batteries. Recycled cathode materials derived from waste generated at our US factories will over time be used at our new factory in Kansas.
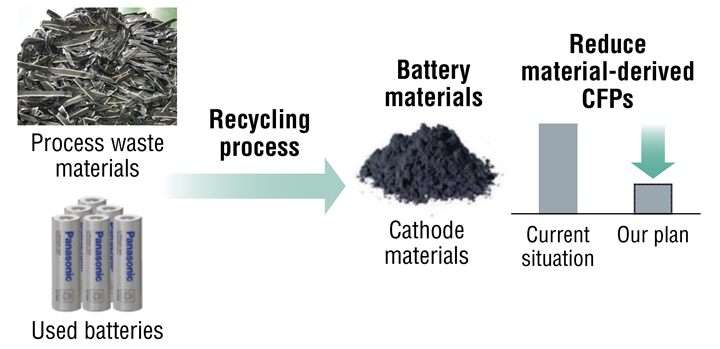
Recycling process for process waste and used batteries
Outside the United States, in 2024 we initiated a partnership with Sumitomo Metal Mining Co., Ltd. and other suppliers to operate a recycling scheme that recycles the cathode material nickel, a rare metal, from battery waste materials, and uses it again as a cathode material in our production processes. From 2026 onwards, we plan to reuse lithium and cobalt, which are other cathode raw materials, in the same way.
Initiatives related to dry batteries
For dry batteries, which are primary batteries that cannot be used repeatedly, we are working to recover and recycle used dry batteries with the aim of unlocking new value.
Initiatives to collect and recycle used dry batteries
In Thailand, we started a partnership with CP ALL Public Company Limited (a convenience store operator) in fiscal 2023 to collect waste dry batteries at 1,000 stores. In Japan, we started a similar initiative in partnership with AEON RETAIL Co., Ltd. in fiscal 2024.
In terms of recycling the collected dry batteries, in Thailand, we partnered with UMC Metals Ltd. starting in March 2024 to start recycling them as materials for steel, while in Japan, we started a recycling initiative with Tokyo Steel Manufacturing Co., Ltd.
We will continue to expand our collection areas and full-scale operations in Thailand and Japan while also expanding the expertise that we have gained to other regions. We are also promoting research and development with a view to future use in dry battery components, aiming to realize “battery-to-battery” recycling.

Dry battery recovery model in Japan
Initiative to turn used dry batteries into fertilizer
In collaboration with TOMATEC Co., Ltd., we have established a process to recycle used dry batteries into trace element fertilizer*1. In the recycling process, we separate the black mass*2 from used dry batteries manufactured by us and then have TOMATEC convert it into compound trace element fertilizer*3. This is our first initiative to recycle dry batteries in the agricultural sector. This is also the first time for TOMATEC to manufacture and sell compound trace element fertilizers derived from battery materials.
In the future, the two companies will work together to expand the use of trace element fertilizers derived from batteries, and further promote resource recycling and environmental initiatives. This is expected to contribute to agricultural development and, in the future, to eliminating social problems such as hunger and poverty.
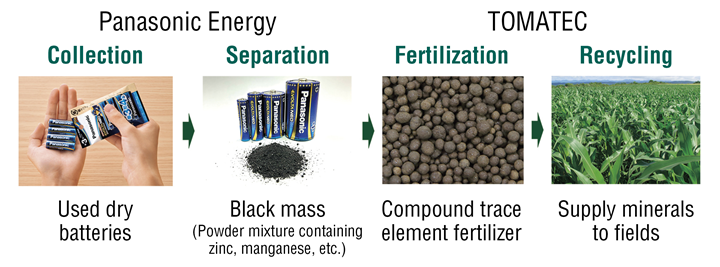
Process for recycling used dry batteries manufactured by Panasonic Energy into compound trace element fertilizer
*1 Fertilizer containing trace elements necessary for plant growth. Trace elements include zinc (Zn), manganese (MN), and iron (Fe).
パナソニック エナジー乾電池由来の微量要素肥料を共同開発、使用済み乾電池を肥料原料にリサイクルするプロセスを確立 (*Japanese-language release only)
*2 Mixed powder containing zinc, manganese, etc.
*3 The zinc and manganese contained in used dry batteries are melted and vitrified, making more easily absorbed by crops.
Promoting the use of recycled materials
We are working together with raw material manufacturers to ensure that our production sites in Japan use 100% recycled materials*4 for their zinc, a key component of the anodes of dry batteries. This recycled zinc accounts for approximately 15%*5 of the body weight of the EVOLTA NEO dry battery, demonstrating our ability to create high-quality products that combine the effective use of limited resources with the reduction of environmental impact.
The use of recycled materials in this way is an important initiative that contributes to the realization of a recycling-oriented society while maintaining the performance of dry batteries. Going forward, we will continue to make effective use of resources, extend their service life, and promote initiatives which will lead to a reduction in environmental impact.
*4 Acquired UL certification (UL 2809) from the raw material manufacturer that the material is made from 100% recycled materials based on the "mass balance method."
*5 Percentage of recycled zinc to body weight.
Increasing recycling
Utilization of recycled materials
In the production of batteries, Panasonic Energy is working to build a recycling scheme throughout the entire supply chain by reducing natural resource consumption and waste, for example by strengthening our efforts to collect and recycle waste materials from the production process as well as used products and utilize them as recycled materials.
Going forward, we will continue to promote the use of recycled materials as electrode materials, aiming not only to decarbonize our products, but also to realize a recycling-oriented society.

Recycling scheme throughout the entire supply chain
Initiatives related to secondary batteries
Initiatives related to collecting and recycling secondary batteries
For secondary batteries, countries around the world are developing legal systems and mechanisms for recycling aimed at using resources more effectively and preventing environmental pollution. In Japan, we are a member of Japan Portable Rechargeable Battery Recycling Center (JBRC), a recycling promotion organization established mainly by Matsushita Battery Industrial Co., Ltd. and SANYO Electric Co., Ltd. (our predecessors). In this role, we engage in collection and recycling of secondary batteries from cooperating stores, municipalities, and businesses nationwide. In fiscal 2025, the industry as a whole collected and recycled 1,400 tons of secondary batteries (around 50% of which were made by our company). In North America, we collaborated with other battery manufacturers to launch the Call2Recycle program, which offers recycling schemes for secondary batteries in the United States and Canada. We are also helping various other countries create the most efficient recycling systems that match the actual recycling infrastructure situation in each country.
Initiatives to establish a recycling scheme
We have signed a purchase agreement with Redwood Materials Inc., a U.S. battery recycling company, for the use of recycled cathode materials for Li-ion batteries for EVs. Under the agreement, we will establish a system to recycle process waste and used batteries into cathode materials for Li-ion batteries. Recycled cathode materials derived from waste generated at our US factories will over time be used at our new factory in Kansas.

Recycling process for process waste and used batteries
Outside the United States, in 2024 we initiated a partnership with Sumitomo Metal Mining Co., Ltd. and other suppliers to operate a recycling scheme that recycles the cathode material nickel, a rare metal, from battery waste materials, and uses it again as a cathode material in our production processes. From 2026 onwards, we plan to reuse lithium and cobalt, which are other cathode raw materials, in the same way.
Initiatives related to dry batteries
For dry batteries, which are primary batteries that cannot be used repeatedly, we are working to recover and recycle used dry batteries with the aim of unlocking new value.
Initiatives to collect and recycle used dry batteries
In Thailand, we started a partnership with CP ALL Public Company Limited (a convenience store operator) in fiscal 2023 to collect waste dry batteries at 1,000 stores. In Japan, we started a similar initiative in partnership with AEON RETAIL Co., Ltd. in fiscal 2024.
In terms of recycling the collected dry batteries, in Thailand, we partnered with UMC Metals Ltd. starting in March 2024 to start recycling them as materials for steel, while in Japan, we started a recycling initiative with Tokyo Steel Manufacturing Co., Ltd.
We will continue to expand our collection areas and full-scale operations in Thailand and Japan while also expanding the expertise that we have gained to other regions. We are also promoting research and development with a view to future use in dry battery components, aiming to realize “battery-to-battery” recycling.

Dry battery recovery model in Japan
Initiative to turn used dry batteries into fertilizer
In collaboration with TOMATEC Co., Ltd., we have established a process to recycle used dry batteries into trace element fertilizer*1. In the recycling process, we separate the black mass*2 from used dry batteries manufactured by us and then have TOMATEC convert it into compound trace element fertilizer*3. This is our first initiative to recycle dry batteries in the agricultural sector. This is also the first time for TOMATEC to manufacture and sell compound trace element fertilizers derived from battery materials.
In the future, the two companies will work together to expand the use of trace element fertilizers derived from batteries, and further promote resource recycling and environmental initiatives. This is expected to contribute to agricultural development and, in the future, to eliminating social problems such as hunger and poverty.

Process for recycling used dry batteries manufactured by Panasonic Energy into compound trace element fertilizer
*1 Fertilizer containing trace elements necessary for plant growth. Trace elements include zinc (Zn), manganese (MN), and iron (Fe).
パナソニック エナジー乾電池由来の微量要素肥料を共同開発、使用済み乾電池を肥料原料にリサイクルするプロセスを確立 (*Japanese-language release only)
*2 Mixed powder containing zinc, manganese, etc.
*3 The zinc and manganese contained in used dry batteries are melted and vitrified, making more easily absorbed by crops.
Promoting the use of recycled materials
We are working together with raw material manufacturers to ensure that our production sites in Japan use 100% recycled materials*4 for their zinc, a key component of the anodes of dry batteries. This recycled zinc accounts for approximately 15%*5 of the body weight of the EVOLTA NEO dry battery, demonstrating our ability to create high-quality products that combine the effective use of limited resources with the reduction of environmental impact.
The use of recycled materials in this way is an important initiative that contributes to the realization of a recycling-oriented society while maintaining the performance of dry batteries. Going forward, we will continue to make effective use of resources, extend their service life, and promote initiatives which will lead to a reduction in environmental impact.
*4 Acquired UL certification (UL 2809) from the raw material manufacturer that the material is made from 100% recycled materials based on the "mass balance method."
*5 Percentage of recycled zinc to body weight.
Waste reduction initiatives
Reduced waste from the factory
We work continuously to reduce waste generated by our factories (the amount of waste going to landfill) to as close to zero as possible and to increase the volume of valuable materials and resources recycled. For the recycling rate (in-house waste) we had previously set as a KPI, almost all of our sites achieved 99% or more. Now that we have a system in place within the Company that can be sustainably maintained, starting this fiscal year, our only recycling KPI will be our recycled material utilization rate.
Initiatives to reduce plastic use
While plastic is an indispensable material in modern society, its impact on climate change and the challenges it poses as a waste material are driving our efforts to reduce plastic use.
As one of our initiatives, we launched dry batteries in “ethical packages” in both Japan in fiscal 2022 and Thailand in fiscal 2023. These packages are designed to reduce packaging materials and eliminate plastics, as products aimed at ethical consumption (consumption activities that consider not only the functional value of products and services but also their ethical value). The introduction of this ethical packaging reduces the amount of packaging materials used (including plastic) by 38–59% compared to conventional products. It also contributes to a reduction in total CO2 emissions throughout the lifecycle of packaging materials, including obtaining raw materials, manufacturing, use, and disposal.
From 2023, we expanded our lineup to include the rechargeable nickel-metal hydride battery “eneloop” and coin cell batteries*6 with ethical packaging. We have also accelerated our business globally, starting with the Asia-Pacific region. Furthermore, in September 2023, we received the Japan Star Award (Minister of Economy, Trade and Industry Award).

Products with ethical packaging
*6 Sold only through certain online shopping websites.
Initiatives to utilize recycled resin to reduce usage
With growing concern for the environment, including reducing waste and CO2 emissions, we are working to reduce the amount of plastic we use by utilizing recycled resins. In response to customer requests to use more recycled resin, we have raised the ratio of recycled resin used in battery pack outer cases from 25% to 50% for some models. This contributes to the reduction of energy required for plastic production and the recycling of plastics scheduled for disposal. Since mechanical properties such as strength and heat resistance are reduced with the use of recycled resin, risk verification was also conducted before introduction. In the future, we will contribute to environmentally friendly activities by expanding the use of recycled resin and other measures.





